It is common knowledge that poisons are harmful, but do you know that helpful poisons also exist? Everything comes in two-way effects, so it is good if we use them in the right way. In the list below, we are looking at a variety of substances in both poisons and venom that we normally avoid. However, you can also find them in medicine bottles and pill boxes as part of treatment as well. Take a look at the helpful poisons in our list and let us know if you have used them.
1Chilean Rose Tarantula Venom
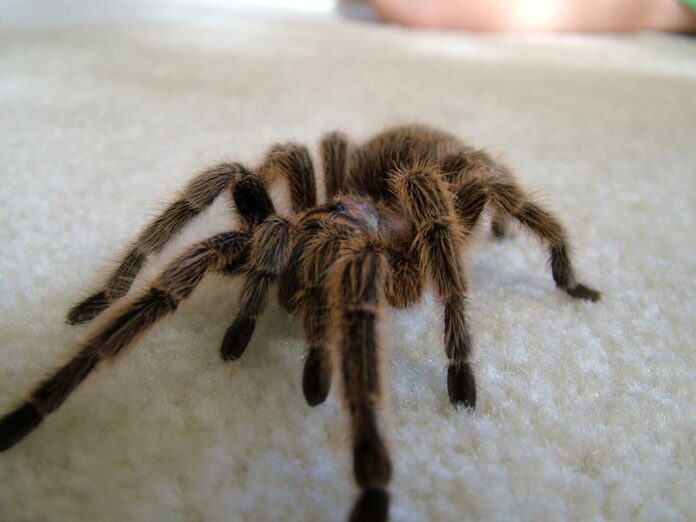

Biophysics from the University at Buffalo are using a protein from the venom of Chilean Rose tarantula to combat death from heart attacks. The walls of your cells have tiny channels that open when the cell stretches, and these channels are responsible for heart muscles. The contraction of heart muscles, to be exact.
When these channels open too wide when heart muscles stretch, they allow a flood of positive ions into the cell. These extra ions disrupt the electrical signals in the heart, causing the organ to fibrillate meaning beats wildly and irregularly. So the protein from the tarantula’s venom binds to these channels which can block the positive ions from passing through. This could ostensibly prevent fibrillation, and hopefully death, if delivered during a heart attack.
2Cone Snail Venom
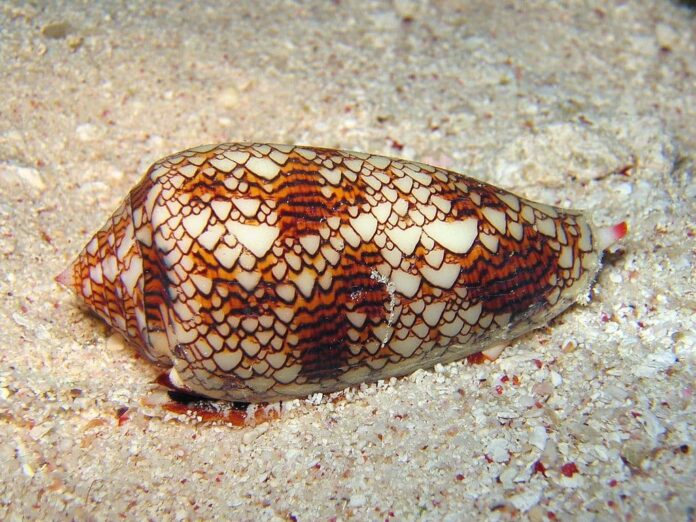

Cone snails are one of the most poisonous animals on earth due to their poison gland that contains neurotoxins. The sting of small cone snails is no worse than a bee sting, but the sting from larger ones can be fatal. The venom of these cone snails is great when it comes to providing a non-addictive pain reliever. The potential is 1000 times as powerful as morphine, and it makes a possible replacement for morphine because it is non-addictive.
So the first painkiller derived from cone snail toxins was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in December, 2004. The name was Prialt, and there are other drugs that are in clinical and preclinical trials such as compounds of the toxin. The estimation is that they may be possible to use in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and more.
3Copperhead Venom
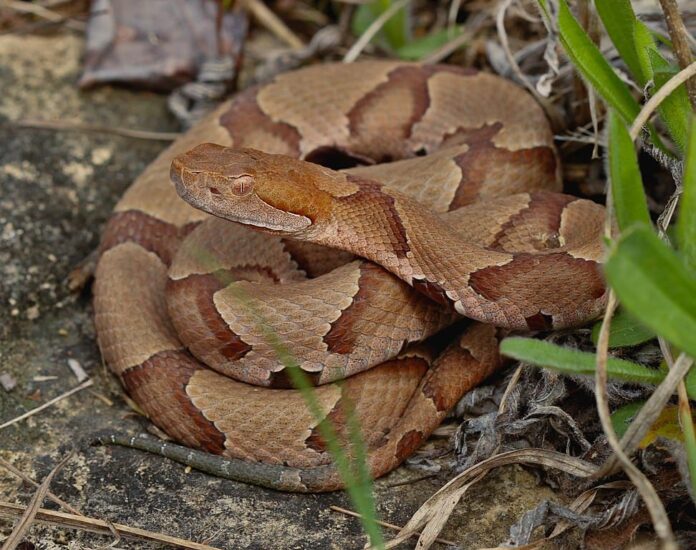

Copperhead is one of the most venomous snakes in the world as well as an ambush predator in the animal kingdom. The venom of the southern copperhead has been found to hold a protein “Contortrostatin” that halts the growth of cancer cells. On top of that, venom also stops the migration of the tumors to other sites in the body. With such potential, doctors expect to use the venom in practical treatment to be a novel anti-cancer drug.
4Deadly Nightshade
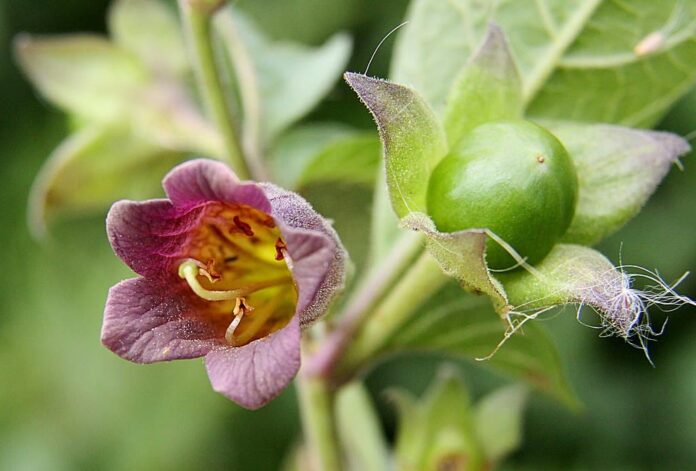

Deadly nightshade contains tropane alkaloids called atropine, and the same poison also exists in jimsonweed, mandrake, and more. People use injections of atropine in the treatment of bradycardia (extremely low heart rate), asystole, and pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest. Atropine’s actions on the parasympathetic nervous system inhibit salivary, sweat, and mucus glands.
This can be very useful in treating hyperhidrosis, and it can also prevent the death rattle of dying patients. Because of its extremely important use in medicine, it has become a core medicine in the World Health Organization’s Essential Drug List. The list consists of the minimum medical needs of a basic health care system, and no doubts why it is one among the helpful poisons.
5Digitalis
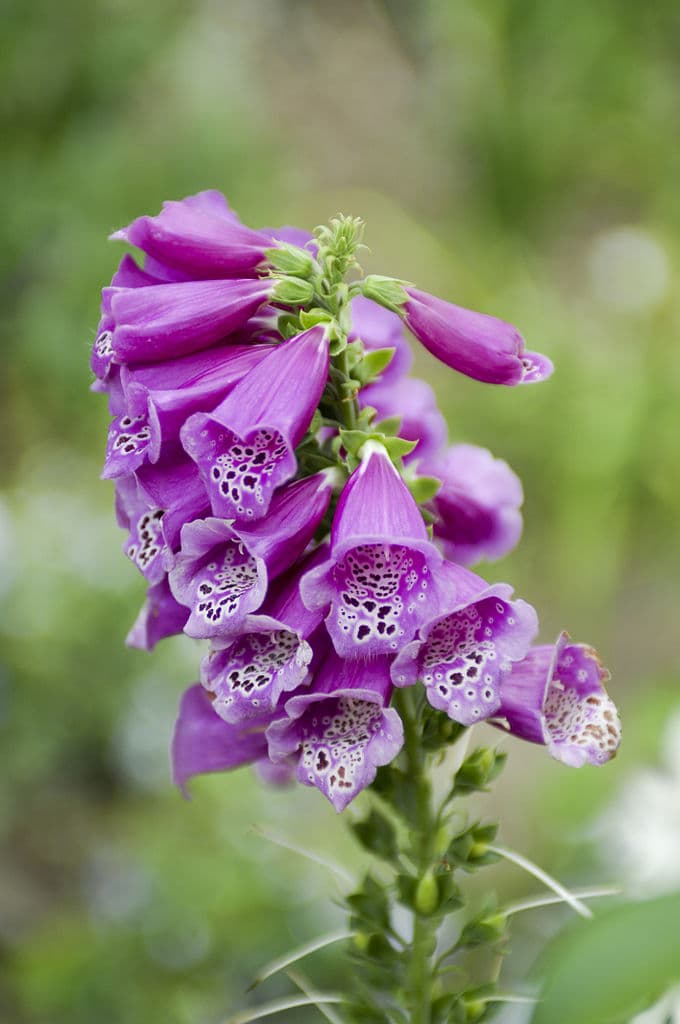

Depending on the species, the digitalis plant may contain several deadly physiological and chemically related cardiac and steroidal glycosides. The entire plant is toxic even the roots and seeds while the leaves of the upper stem are particularly potent. With just a nibble of the upper stem is deadly enough to potentially cause death to a person. Medicines from foxgloves are called Digitalin which people used to increase cardiac contractility, and as an anti-arrhythmic agent to control heart rate. Therefore, it is often prescribed for patients with atrial fibrillation especially if they have been diagnosed with heart failure.
6Ergot
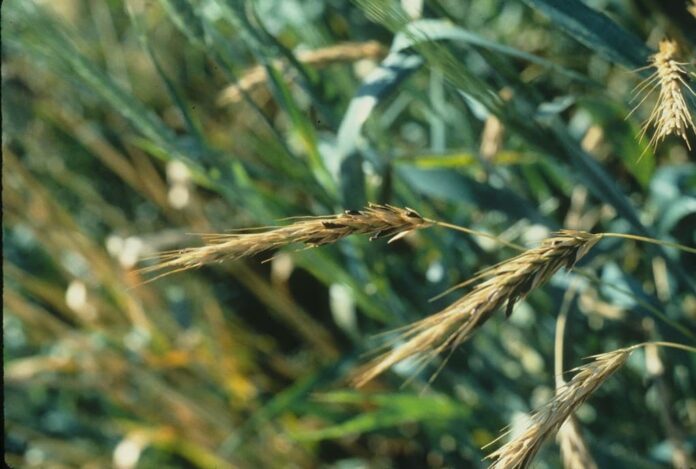

Man has a long history with ergot which is a fungus that infects rye (transferred to humans who eat the grain). Ergotism causes hallucinations and attendant irrational behavior, convulsions, and even death along with other symptoms like strong uterine contractions, nausea, and unconsciousness. Consumption can lead to the amputation of limbs that are damaged by the fungus.
The advantages of ergot are that they can induce abortions and stop maternal bleeding after childbirth with controlled doses. Ergot alkaloids are used in products like Cafergot (containing caffeine and ergotamine or ergoline) to treat migraine headaches. People also used them in a variety of treatments for Parkinson’s disease since the middle ages.
Ergotism has even been blamed for the extremely bizarre dancing plague which struck Europe in the 1500s. However, they are actually very helpful and useful when used in a proper way.
7Hemlock

In the poison world, Hemlock is one of the most widely known poisons that contains coniine which is the most important and toxic alkaloid. Coniine is a neurotoxin that disrupts the workings of the central nervous system which is toxic to humans and all classes of livestock. More than that, coniine causes death by blocking the neuromuscular junction in a manner similar to curare. That results in ascending muscular paralysis with eventual paralysis of the respiratory muscles which leads to death. The death is the result of the lack of oxygen to the heart and the brain.
Despite all the deadly reputations and effects, hemlock is one of the helpful poisons. People have used them as a sedative and for their anti-spasmodic properties as part of medical treatment. The Greek and Persian physicians for a variety of problems such as arthritis and more. People also use the leaves, roots, and seeds of hemlock to make medicine for breathing problems like bronchitis, whooping cough, and asthma. Hemlock is also useful for painful conditions including teething in children, swollen and painful joints, and cramps.
8Warfarin
Warfarin is an anticoagulant, and it was initially marketed as a pesticide against rats and mice. A few years after its introduction, warfarin was found to be effective and relatively safe for preventing thrombosis and embolism. So it was approved for use as a medication in the early 1950s, and it has remained popular ever since.
Warfarin is the most widely prescribed anticoagulant drug in North America, but it has several shortcomings despite its effectiveness. Many common medicines interact with warfarin and its activity has to be monitored by frequent blood testing. Due to its potential, warfarin is still popular still today for both medication and pesticide purposes.
9Wolfs Bane
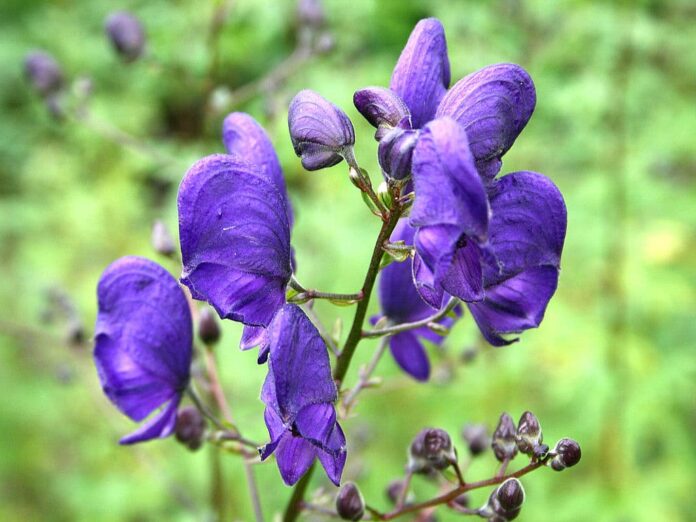

The roots of aconitum Ferox aka wolfsbane supply the Nepalese poison called bikh, bish, or nabee. It contains large quantities of the alkaloid pseudaconitine which is a deadly poison. Also, aconitum palmatum yields another of the bikh poisons which people used in Western medicine preparations until the middle of the 20th century. Now people replace them with safer and more effective drugs and treatments instead, but there are still people use them.
Some used the poison to slow the pulse, as a sedative in pericarditis and heart palpitations.
More than that, it is also used as well diluted as a mild diaphoretic or to reduce feverishness. The feverishness normally exists in colds, pneumonia, quinsy, laryngitis, croup, and asthma due to exposure. The interesting part is that people used wolfsbane flowers to identify supposed werewolves. If the flower cast a yellow shadow on the suspected shape-shifter’s chin, the werewolf test was positive.
10Yellow Scorpion Venom
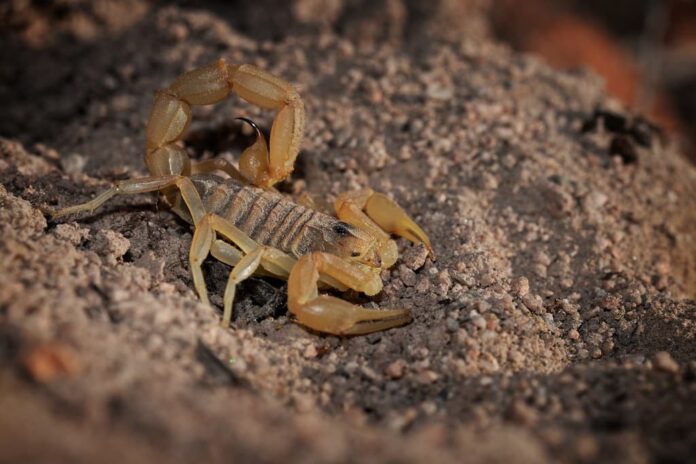

Venom from menacing arachnid like scorpions and spiders are very helpful in the treatment of cancer. Researchers at the Transmolecular Corporation in Cambridge, Mass., have isolated a protein that occurs in the venom of the Israel yellow scorpion. This protein has been shown to seek out and bind itself to the types of cancerous cells found in gliomas. Gliomas is a type of brain cancer that is particularly difficult to treat.
When introduced into the bloodstream, the protein seeks out glioma cells and binds to them carrying the radioactive solution along. The solution then destroys the cell, and with enough treatments, treatment for cancer will be possible to cure.
Related Post: Deadliest Poisions



