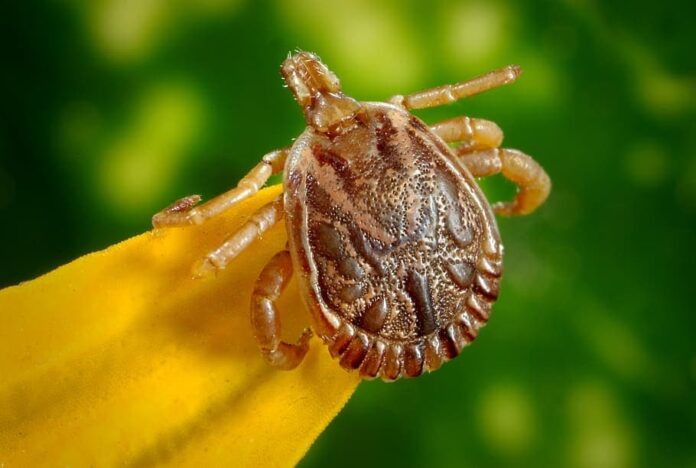
Ectoparasite is a new term that describes organisms that attach or burrow themselves into the skin of their hosts. The worst part is that they remain there for relatively long periods of time as they feed their host. While not killing the hosts, ectoparasite can cause allergic reactions, anemia, irritation, morbidity, mortality, and more. The list below consists of some of the most common ectoparasite pathogens that you might want to know.
Animal Ectoparasites
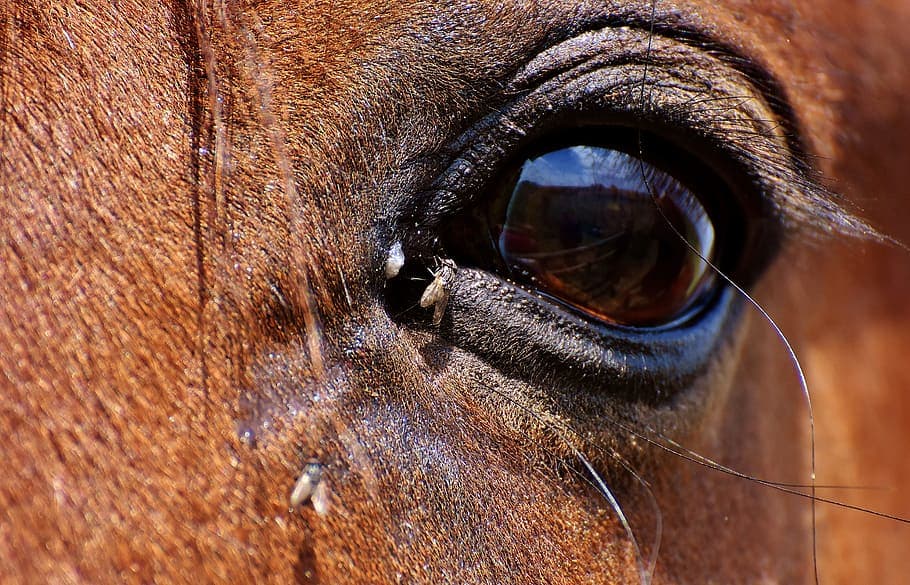

The thing about animal ectoparasites is that they inhabit the skin or skin surface of the animals. Their target hosts could be cattle, house pets, and more. These ectoparasites depend on their hosts for sustenance, maturation, and multiplication before they find their next victims. Some of the most common animal ectoparasites are below so let’s take a look.
1Blood-Feeding Fly
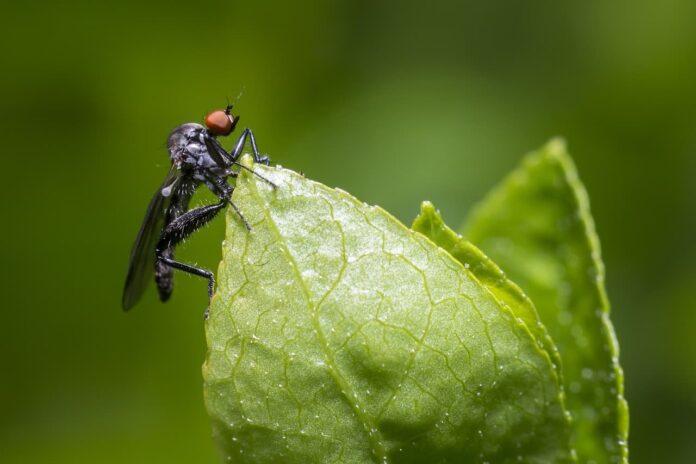

We are talking about a few fly species that suck blood including black fly, deer fly, horse fly, sand fly, and stable fly. These flies have the ability to suck the blood of either animals or humans, some can do both. Blood-feeding flies don’t necessarily live on the host’s skin but they always come back for more. Let’s see a quick brief of them below:
Blood-Feeding Flies
- Black Fly: lives in moist environments, and it is common near creeks and rivers. This species does not transmit disease to humans but their bites can cause deaths due to allergic reactions. The only time when they can threaten the lives of humans and livestock is late spring and early summer. That is when they present in very large numbers when they attack the victim’s head and where clothing fits tightly. The bites often cause considerable bleeding and swelling along with itchiness and slow healing.
- Deer Fly: also goes by the name green-headed fly or yellow fly, and it sucks blood from both animals and humans. The bites from large populations of these flies can reduce milk production from beef and dairy cattle. Their bites can be very painful and can cause allergic reactions as well.
- Horse Fly: is large and heavy-bodied, and it has large eyes. The females are fast and strong fliers, and they suck blood. As the name suggests, these flies target horses so their bites can interfere with the grazing of horses. The horses under their attack will bunch together or injure themselves as they run to escape the flies.
- Sand Fly: is a small bloodsucking gnat, and it is small enough to enter houses through normal window screening. Mostly, they feed on the blood of amphibians, birds, mammals, and reptiles at night; and penguins are reportedly their favorite.
- Stable Fly: looks like a house fly but sucks the blood of both animals and humans. These flies have a bayonet-like proboscis that projects forward from their head. The thing is that they usually bite about 130 to 45 centimeters from the ground.
2Mite
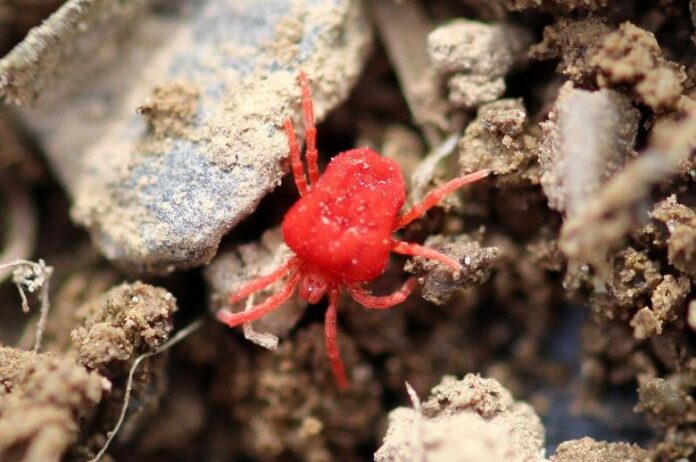

Mites are small invertebrates that infest and parasitize domestic animals, causing diseases and production loss. Usually, domestic animal mites cause various skin disease types while some infest other organs. Their life cycle begins with eggs that are laid on the vertebrate animal host or within the host’s environment or nest. Ectoparasite mites typically transfer from one host to another by crawling between hosts that are in close contact.
3Myiasis-Causing Fly
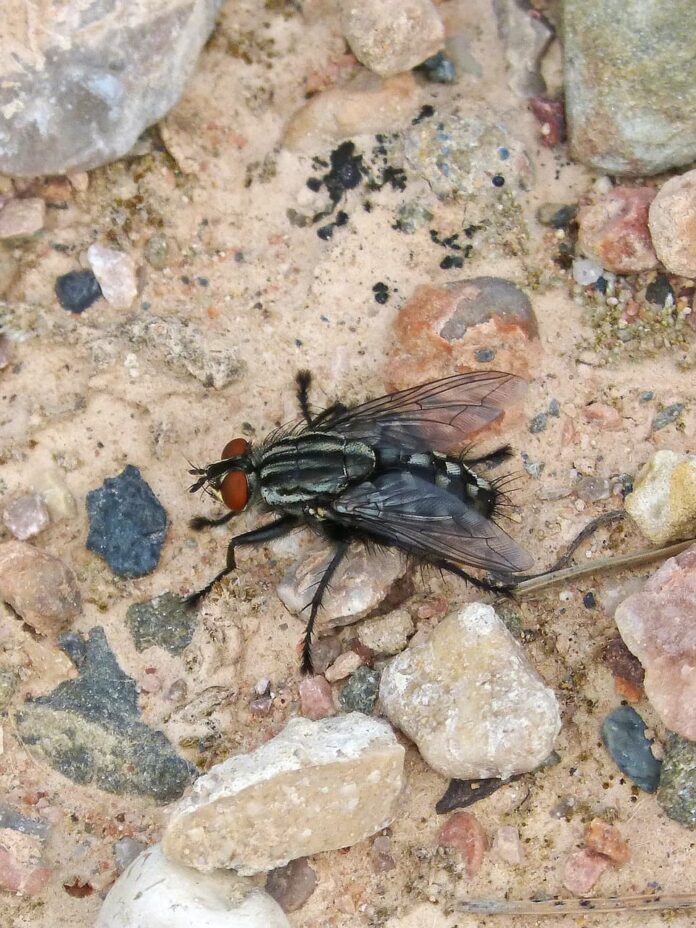

The term myiasis refers to an infestation of the skin-developing larvae of the botfly variety. Myiasis is the parasitic infestation of a live animal’s body by fly larvae (maggots) that grow inside the host. Some lay their eggs in open wounds, and the eggs take 8 hours to a day to hatch. Their maggots feed on the host’s skin or tissues using their mouthparts as they grow, causing open sores. Along with that, the botfly, blowfly, and screwfly can also create an infestation on a host’s unbroken skin.
4Tick
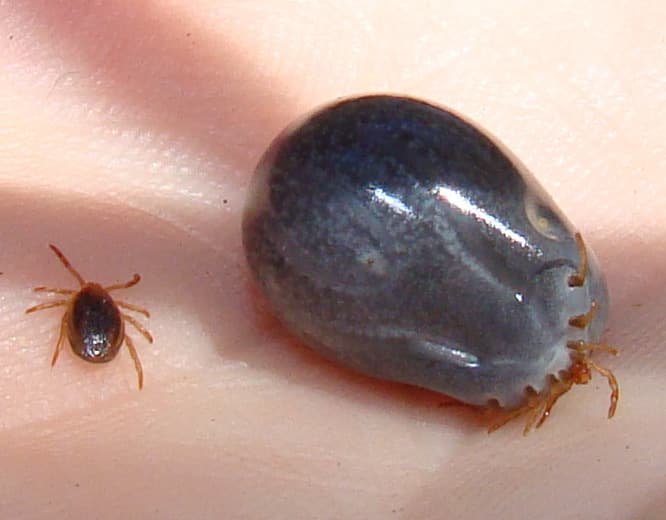

Ticks are one of the most common ectoparasite pathogens that suck blood from animals. Their bodies become darker and larger when filled with blood, and they also appear on pets as well. Ticks don’t fly or jump, they climb or drop on the animal’s coat as it passes by. Normally, ticks bite and feed on the cat or dog for up to a few days. They will drop off once they have enough, and they can give the animals a disease during those few days.
Human Ectoparasites
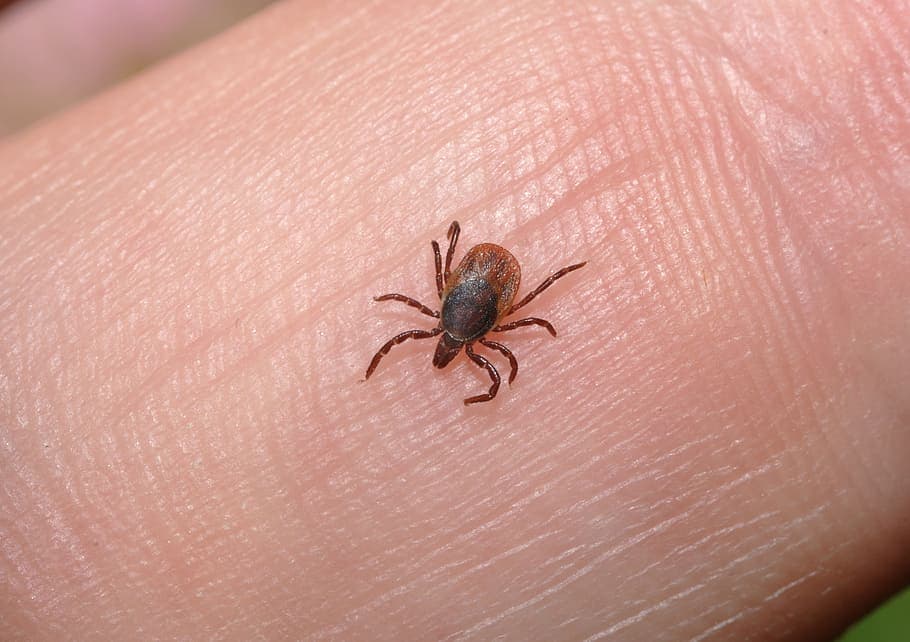

Not different from animal ectoparasites, human ectoparasites are quite the same when it comes to the process. These diverse groups of organisms infest the skin of human beings, sucking blood and causing potentially harmful diseases as well. The symptoms could be irritation, itchiness, and other discomforts. Human ectoparasites that people normally come across include:
5Bed Bug
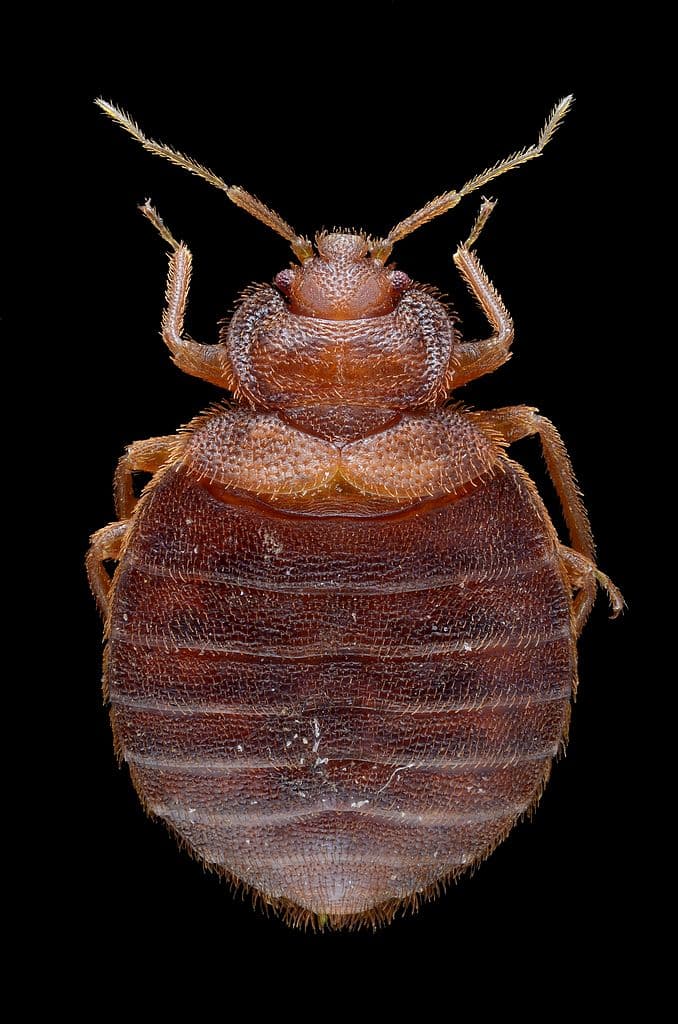

Probably one of the most gross ectoparasite beings that we all disgust and hate. These pests feed on humans while they sleep, causing itchiness and red bumps that are so irritating. People don’t wake up at night during the bites because a bed bug’s saliva contains a mild anesthetic. Simply put, the victim cannot feel the pain that allows the bugs to feed to their content.
Getting rid of bed bugs is a lot of work, especially after the infestation because discovering them is usually a little late. Bed bugs can live literally anywhere, being able to withstand temperatures from nearly freezing up to 120 degrees Fahrenheit. This is why it is not a doubt that this ectoparasite can resist pesticides. The only good thing is that bed bugs don’t spread diseases so at least that is something nice to know.
6Body Lice
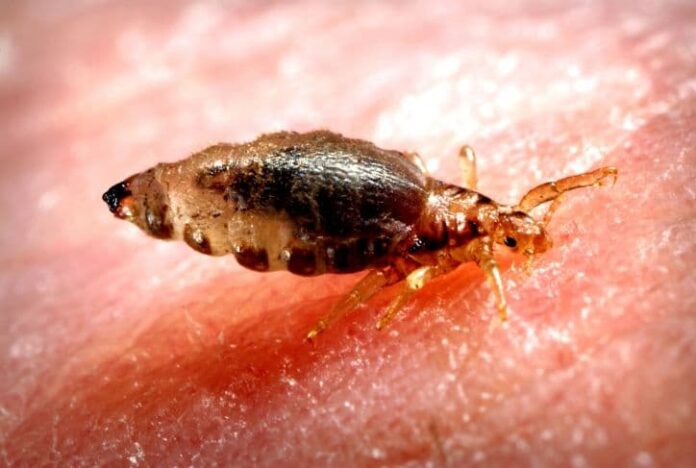

This is a tiny insect that has the size of a sesame seed that lives in people’s bedding and clothing. These lice are most common in crowded and unhygienic living conditions, spreading by direct contact with an infected person’s clothes. Body lice travel to people’s skin several times a day to feed on blood, usually around the armpits, groin, neck, shoulders, and waist. The bites can cause intense itching along with blood and crust on the biting sites.
Well, unlike bed bugs, body lice bites can spread certain types of diseases and can even cause epidemics. Body lice can irritate your skin if you itch when they scratch and dig to feed your blood. If you are infested with body lice for a long time, you may also experience skin changes such as discoloration and thickening. Sometimes they can also carry and spread bacterial diseases like relapsing fever, trench fever, and typhus. When discover on time, bedding and clothing that have been infested should be laundered in hot soapy water.
7Flea
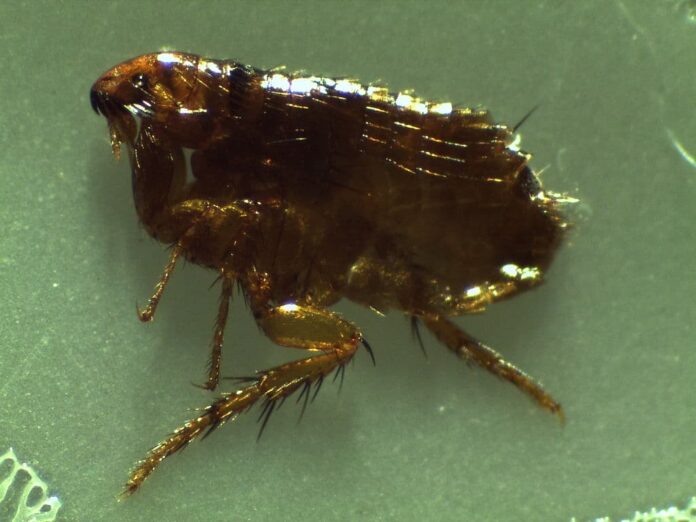

Both animals and humans are at risk of fleabites, and the bites can be itchy and painful. A fleabite on a human may appear as a small discolored bump that may present with a halo or ring. Fleabites may also appear in a straight line or as a cluster of many bites, usually around ankles, feet, or legs. Without control, fleas can spread across the body and bite anywhere, especially on people with dense hair on the chest or legs.
The bites can trigger allergic reactions but do not have a serious impact on a person’s health. However, fleas can carry human diseases; the most famous example was the plague. Humans are the secondary options for fleas because we don’t make good hosts. Only hungry adult fleas without a host would bite us. You should regularly clean and vacuum your bedding, floors, furniture, and skirting boards to reduce the risk of flea infestation.
8Head Lice
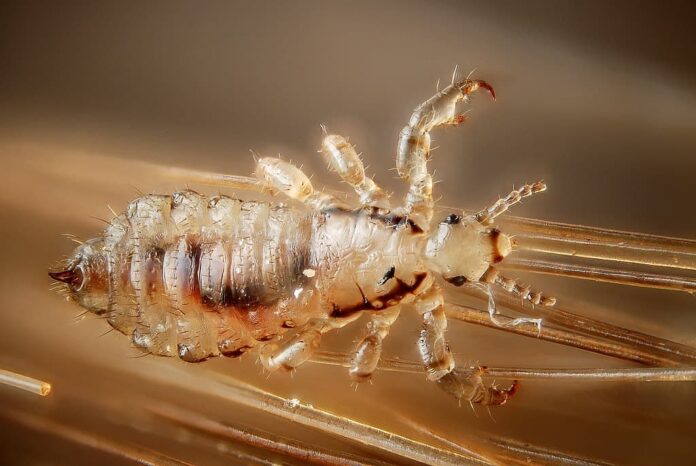

Oh the horror, head lice are very common in young children before spreading them to their families. It is the ectoparasite that can be found on people’s eyebrows, eyelashes, and of course, heads. Head lice live close to the human scalp and feed on their blood several times a day. The only way to make sure that a person has head lice is by combing the hair with a fine-toothed comb. Once you see live lice, then you know that more of them are there. The good thing is that head lice removal is easier now with various methods available.
9Pubic Lice
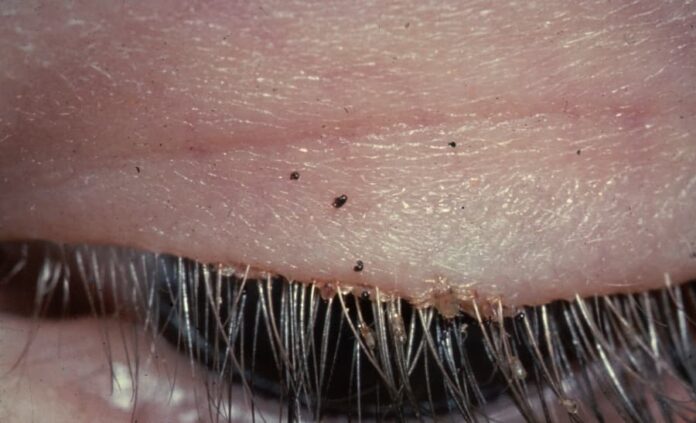
Commonly known as crabs, pubic lice are parasitic insects found primarily in a person’s genital or pubic area. These ectoparasite organisms also live in the hair around the armpits, beards, eyebrows, eyelashes, and mustaches. The signs and symptoms of pubic lice are itching in the genital area and visible crawling lice or nits (eggs). Pubic lice are most common in adults and are usually spread through sexual contact. Sometimes people can also get them by close personal contact or contact with bed linens, clothing, or towels used by an infested person.
Pubic lice suck blood periodically, and their bites typically cause irregular blue spots in the skin around the bite site. The blue spots develop a few hours after the bites and can last for several days. However, not all bites cause this reaction. Female pubic lice lay many eggs on a single human hair. These eggs will hatch after 7-8 days and will reach adulthood in the next 13 to 17 days. Treatment is available, and patients should seek treatment as soon as possible.
10Scabies
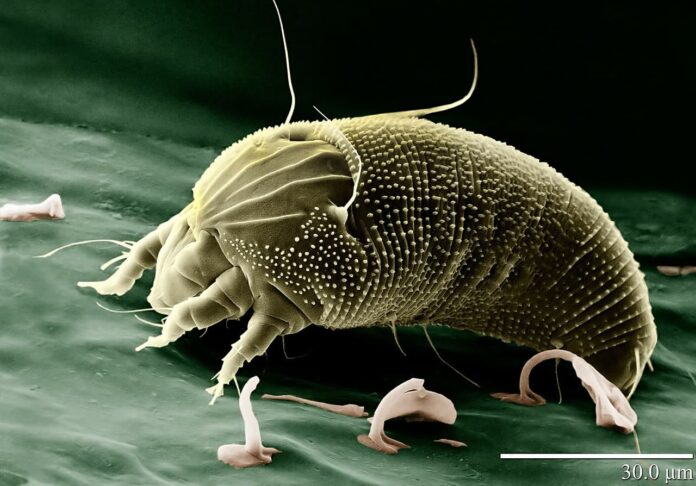

We cannot have a list of ectoparasite without scabies, the itch mite that causes infestation in the human skin. A scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Tiny burrows are sometimes visible on the skin, appearing as tiny raised and crooked grayish-white or skin-colored lines. On a person, scabies mites can live for as long as 1 to 2 months. Off a person, they usually do not survive more than 48 to 72 hours.
The most common symptoms are intense itching (especially at night) and a pimple-like skin rash. At the same time, the rash can also include tiny blisters and scales as well.
A person with scabies has thick skin crusts that contain large numbers of scabies mites and eggs. That person is very contagious to other people as they can spread the infestation easily by direct contact or item contamination. Treatment for scabies is available at the hospital, and only with a doctor’s prescription.
Related Post: Things You Should Know About Disease Vectors




